The Global warming I F K

Global warming refers to the increase in the mean global temperature
of the earth due to green house effects. But the term is most often used to refer to the warming predicted by computer models to occur as a result of increased emissions of green house gases.
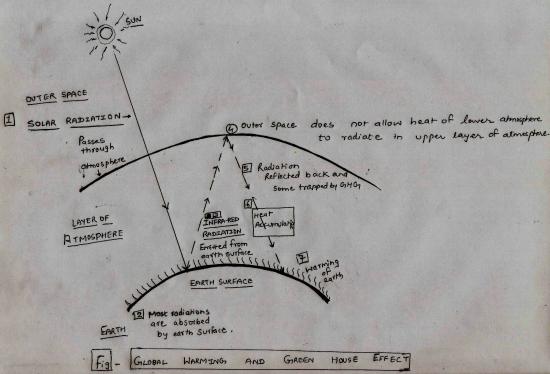
The increase in green house gases in the atmosphere is making a layer. This layer allows sunlight to enter into the atmosphere, and is absorbed by the earth surface. This absorbed energy is also radiated back to the space. The earth atmosphere contains gases which trap some of the outgoing radiation and thereby warm the earth. These gases are known as Green House Gases (GHG) and the phenomenon is called Green house effect, leading to global warming.
GREEN HOUSE GASES.
Green house gases effect is due to some gases known as Green House Gases (GHG) present in the lower atmosphere of the earth. They are-
-Carbon-di-oxide (co2)
-Methane (ch4)
-Nitrous oxide (N.O)
-Ozone (o 3)
-Chloro-flouro-Carbon(CFCs)
-Halons
– Water vapor
The increase in the quantity of green house gases in the atmosphere can reinforce the green house effect & lead to global warming. The main GHG differ in the intensity of their heat trapping and thus their ability to affect the radiation balance of the earth. CFCs and N.O are many times more potent than same quantity of Co2 & methane. However Co2 is the largest contributors to the Global warming as it hold the largest share in the atmosphere.
1) CFCs- are chemical used as refrigerants, propellants, solid foams, aerosols etc. These are totally man made GHG, which are very low in the atmosphere but their heat trapping capacity is 100 times more than co2. It is increasing @ 5% per annum ( p .a ). It is banned under Montreal protocol.
2) Methane-It is 20 times more effective than Co2 and is increasing @ 1% p.a. Largest source includes natural wetlands, paddy field, livestock and insects, biomass burning and coal mining.
3) Nitrous Oxides- It is increasing @ 0.3% p.a and contributes to 5% of global warming. It is released due to biomass burning, fossil fuel consumption, use of fertilizers and other natural processes.
4) Carbon –di- oxide: Co2 is a natural constituent of atmosphere. Its normal concentration is 0.03%, and is not considered as pollutant. However human being because of his anthropogenic activities is adding large quantities of Co2 in the atmosphere.
Green plants by the process of photosynthesis balance the amount of Co2 in the atmosphere to a great extent. But because of increasing burning of fossil fuels & depletion of forest cover (deforestation), the amount of Co2 in the atmosphere has increased by 15% in the past 100 years. This increase in Co2 will lead to increase temperature of the earth because of Green house effect.
Concentration of Co2.
At industrial revolution – 250 ppmv (part per million by volume).
In 1991- 311ppmv
In 2007 – 430 ppmv
By 2050 – 550ppmv.
There appears to be positive co-relation between rising level of Co2 and rise in Global Mean Temperature (GMT)
E.g.- Between 1860 to 1986 – GMT increase by 0.7degree centigrade.
During 20th century – GMT increase by 0.4 degree centigrade.
Co2 is increasing @ 0.05% p.a and increases the earth temperature by 50 % .
5) Ozone (O3) – Tropospheric ozone is increasing @ 0.5% p.a in the atmosphere. Ozone is formed by light dependent reaction between nitrogen –di-oxide (No2) and Hydrocarbons. It may also be formed by No2 under U.V ( ultra violet ) radiation effect. Its contribution to global warming is 2%.
6) Water vapor- Methane gas increases stratospheric water vapor on oxidation. The rise in the Water vapor is really more important source of Green house effect than the direct effect of Methane.
Evidences of Global Warming.

1) The Larsen Shelf (ice caps)- 2000 sq. km area in the northern tip of Antarctica is broken up into two pieces in January 2005.
2) Wordie Shelf, which covers 2000 sq. km collapsed in March 2002.
In Artic too the story is similar one, the thickness of the ices which covers the water near the North Pole has been progressively thinning over years. Now ice free water stretch can be seen in North Pole.
3) The occurrence of extreme weather phenomenon in recent years such as – floods in Britain, frequent forest fires in Europe, Australia and Amazon, unprecedented colds in Siberian regions.
4) More frequent and greater intensity of El – Nino.
(Earlier once in 7years & now once in 5 years with greater intensity).
5) Rising summer temperature in both northern and southern hemisphere. (in past 5 years successive summer being more hotter than preceding summer).
6) Effect on coral life in tropical sea.
E.g. palk- strait coral life being destroyed completely.
7) Frequent warm spells heat waves & heavy rainfall.
8) Increase in drought, tropical cyclone & extreme tides.
9) Rising global mean temperature (1.1- 6.4 during 21st century)
10) Rising sea level (between 18 – 59 cm).
Major GHG emitters
US – 24.3%
E.U – 15.3%
CHINA – 14.5%
RUSIA – 5.9%
INDIA – 5.1%
JAPAN -5%
Impacts of global warming.
1) Rise in the mean sea level up to 1 meter in next one hundred years due to melting of polar ice caps with the rise in global temperature.
Many costal areas ( Bangladesh, Bangkok, Mauritius, Venice etc), islands and low lying areas around the world will submerged under sea water resulting in massive human & economic dislocation.
2) Major changes in water distribution & impact on water resources.
The flow of water in streams located in high altitudes & South East Asia will increase while it will decrease in central Asia, South America, Australia & Mediterranean region. Higher evaporation rate due to increased temperature will lead to shortage of water need for irrigation.
3) Change in rainfall pattern.
In tropical regions there will be increased rainfall, but will have uneven distribution. So it will pose the problem of flooding & drought like situations simultaneously. This change in precipitation will have impact on agriculture & vegetations.
4) Change in Global wind pattern & extreme climates.
Drought and Desertification will increase in tropical regions while more rainfall may be expected in temperate regions. This change in wind pattern will lead to uneven distribution of rainfall. Therefore in future deserts will receive more rainfall and agricultural areas will receive less rainfall. These changes will lead to large scale migrations which in turn affect the social, economic & Political skeletal of human society.
5) Major impact on Flora and fauna is due to the change in weather pattern.
– Loss of species diversity.
-Dwindling phytoplankton & Zooplanktons population.
-freshwater fishes are migrating to pole ward direction; many species of fishes are becoming extinct.
-population of pacific salmon dropped since 1997-98
– Polar bear in Hudson Bay having fewer cubs.
– Dwindling population of penguins due to habitat destruction.
6) Adverse effect on natural ecosystems.
Forest, wetlands, lakes, mangroves, grassland, coral reefs etc are severely threatened.
Rise in sea temperature poses an adverse impact on coral reefs, which will suffer from loss of algae that color & feed them. Warm oceans cause the process of bleaching which destroys the most productive ecosystem.
7) Rise in public health problems.
-Rising sea will contaminate freshwater with salt.
– According to W.H.O, Global warming will increase the incidence of respiratory & Cardio-vascular diseases.
-Higher level of tropospheric ozone, with strong sunlight & warm temperatures could worsen respiratory illness.
-Heat related death due to frequent hot spells.
– Increase in vector borne diseases such as malaria, filarial, dengue, yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis etc.
-Reduce food production due to frequent flood & storms, which in turn will reduce food production, thus giving rise to malnutrition problems.
8) Food insecurity- Global warming has important effect on agricultural productivity. El-Nino will become more frequent, thus leading to drought in Asia, Africa, Australia & Floods in North America thereby decreasing agricultural productivity.
9) Increased Frequency of Natural Hazards.
Increase precipitation will lead to increase hazards of floods, landslides avalanches & Soil erosions.
10) Socio – economic impacts of global warming.
Physical infrastructure will be more affected by climate change. Large scale migration of people due to flooding, landslide & rise in sea level coupled with uneven rainfall & extreme weather conditions. Thus population density will increase & will affect the quality of life of the people.
Measures taken to prevent global warming.
Global warming is a global phenomenon so measures are required at global level.
1) UNITED NATIONS FRAMEWORK CONVENTION ON CLIMATE CHANGE (FCCC) – was concluded in 1992 at Rio EARTH SUMMIT,Brazil.
All the countries that signed the convention agreed (voluntarily) to reduce Green house gas emission to 1990 level by 2000AD. However convention did not create a binding legal obligation & it could not bring down the desired level.
2) KYOTO PROTOCOL, DEC 1997.
It was signed as part of COP-3 (3rd conference of parties to FCCC) at Kyoto, Japan in December 1997.This conference is also known as “Green- House Conference “.
Six GHG (CO2, METAHNE, NITROUS OXIDE, HFC, PER-FLOURO-CARBON & SULPHUR HEXACHLORIDE were declared responsible for global warming.
It was the first legal binding measure to curtail emissions of GHG by developed countries.
– By 2012 developed countries would reduce their collective emissions by 5.2% from 1990 levels, with each country being committed to a particular figure like- E.U- 8%, USA- 7%, JAPAN-7%. The developing countries are not under the obligations to curtail their CO2 emissions but they are required to assist the developed countries to meet their targets by the process of Clean Devolvement mechanisms (CDM) which is an instrument of North – south co-operation.
– Under CDM- developed countries can assist the developing countries in cutting down their emission levels and any such reduction achieved in developing countries shall be credited to that developed countries.
– The protocol provides for imposition of Economic sanctions, if a member country fails to meet its obligations under the protocol.
– To make protocol effective- the approval of at least 55 nations are necessary.
3) BONN AGREMENT.
All countries except USA (major polluter) have signed the Kyoto protocol.
4) WORLD SUMMIT ON SUSTAINABLE DEVLOPMENT- JOHANNESBERG (SOUTH AFRICA), SEPT. 2002.
– Could not found any substantial measures check to global warming.
5) KYOTO PROTOCOL, come into force on February 16, 2005 with RUSSIA signing the treaty (increasing the participation nations to 61%)
6) THE PONZAN CONFERENCE ON CLIMATE CHANGE, Poland, 2008.
The Ponzan conference on climate change fails to reach at a substantive decision and produce an elaborate and comprehensive treaty on climate change. The undone tasks and the unsolved issues relating to greenhouse gas emissions, climate change adaptation strategies and clean technologies may well be taken up in the next year’s Copenhagen conference in December.
The Ponzan summit aiming to reach at a global consensus to create a road map to tackle climate change issues after 2012, when the first commitment period of the Kyoto protocol expires.
CHALLANGES TO GLOBAL WARMING.
1) The biggest polluter (US) rejected the emissions cutbacks & accepted only a proposal to enter an exploratory global dialogue. It believes as mandatory energy cuts would harm the U.S economy.
2) Efforts of fast growing economies like India and China is still far from satisfactory.
3) Australia believes that only a comprehensive agreement over this issue can yield results.
4) Kyoto protocol provisions applicable to those nations that ratify it. (Not binding to all nations).
5) Monitoring system & Implementation is vague.
6) No stringent punishment & further there is no financial penalty.
Solutions to tackle Global warming.
1) Firm decision and bold commitment by developed nations.
2) Clear cut goals to save the burning globe.
3) An international organization must monitor and maintain a data base of Carbon foot prints of respective nations.
4) Stringent punishment & financial penalty must be imposed to those country which fails to reduce their emissions levels within stipulated time.
5) Ocean which hold the key to manage Global warming should be highlighted, as ocean is the main sink of Co2.
6) The very concept- Development at the cost of environment & polluters should pay must be given importance.
7) Developed countries should provide technology know how and resources to the developing countries for producing clean energy. ( NORTH- SOUTH COOPERATION)
8) Apart from CDM, other tools such as Green taxation, Green Belt Movement etc must be encouraged.
9) Shifting towards alternative and substitute to fossil fuels and use of renewable energy such as solar, winds etc must be encouraged.
10) International, National and Regional media must highlight the ill effects of Global warming.
11) International Fora such as U.N, G-8, ASEAN, NAM, APEC etc must act as a platform to highlight this cause.
12) International agencies and N.G.Os should took up this issue and must act as a pressure group.
13) Community development program to create awareness among the masses.
14) In school curriculum Environmental topics must be added to their course
15) Award and incentives to those countries who follows the emission norms.
16) Formation of Eco clubs, Science clubs etc.
CONCLUSION.
To sum up we can say that these half hearted attempt will only add to confusion. The need of the hour is clear, time bound & specific commitment by developed/ industrialized economies to take the lead & also rope in emerging economies to tackle this menace.
By- MD. IFTAKHAR ALI
E-MAIL- [email protected]
–




